Kifune Shrine is a lovely little shrine in three parts in the north-eastern part of Kyoto. An exact foundation date of Kifune Shrine is not known, but it is estimated to be around 1500 years old. It is known, however, that in 818 the emperor visited the shrine to pray for the end of a draught. Kifune enshrines Taka-okami-no-kami and Kura-okami-no-kami (both seen as the manifestation of one serpent dragon god, who controls the rain), and Iwanagahime (the goddess of matchmaking).
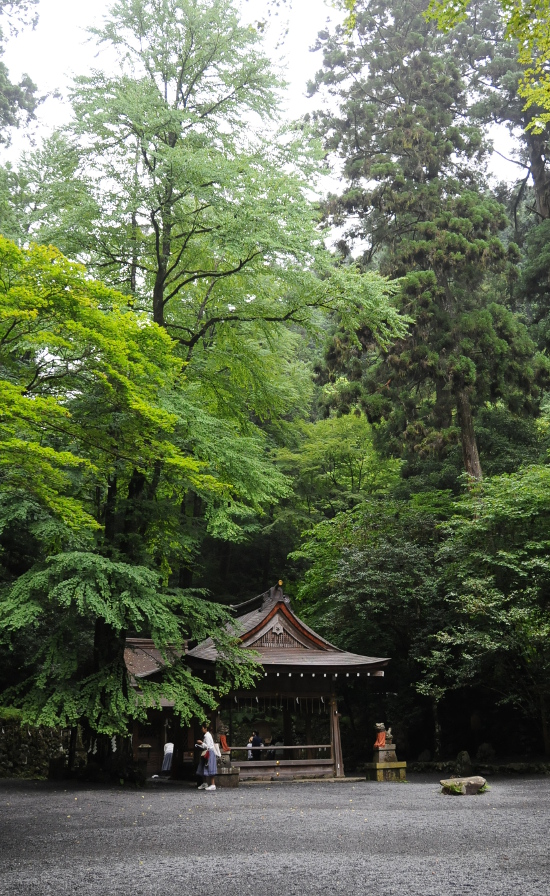
 The first thing one sees of Kifune shrine is a red torii on the left side of the road through the village. Behind it, there are prominent, lantern-lined stone steps, leading up to the Honguu outer shrine. Behind the gate on top of the steps lies the honden, the main building of the shrine, which is built in the nagare zukuri style with a characteristic, beautifully curved roof. Most of the events of Kifune shrine take place in the little square before the honden, and this is also where you can buy omamori charms and omikuji fortune slips.
The first thing one sees of Kifune shrine is a red torii on the left side of the road through the village. Behind it, there are prominent, lantern-lined stone steps, leading up to the Honguu outer shrine. Behind the gate on top of the steps lies the honden, the main building of the shrine, which is built in the nagare zukuri style with a characteristic, beautifully curved roof. Most of the events of Kifune shrine take place in the little square before the honden, and this is also where you can buy omamori charms and omikuji fortune slips.
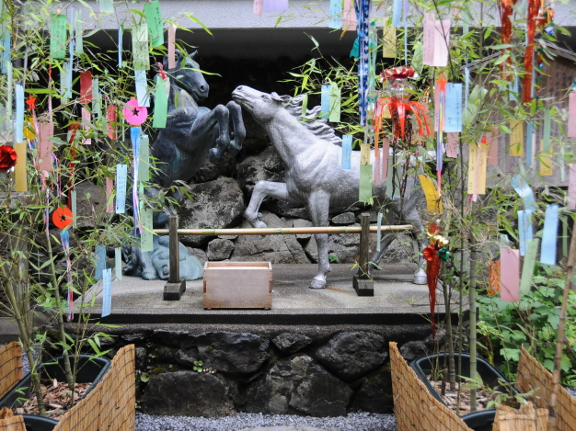
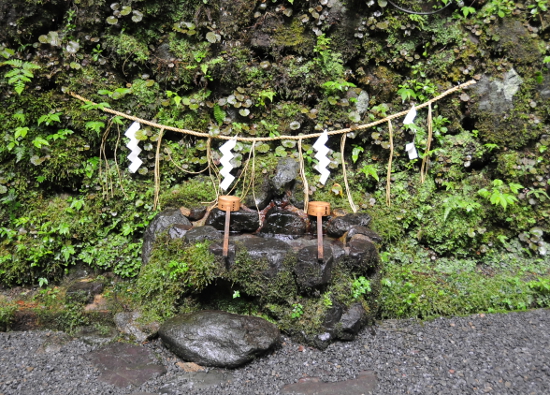 Leaving the honden and turning left, there are two large horse statues. In the old times, when the emperor still lived in Kyoto, he used to send horses to Kifune shrine as offering to the god of rain. A black horse was sent as a prayer for rain to come, and a white horse was sent for the rain to stop. In modern times, it became troublesome to give and take care of many horses, so this may be the reason for the wooden ema tablets with horse images that are presented as prayer offerings nowadays.
Leaving the honden and turning left, there are two large horse statues. In the old times, when the emperor still lived in Kyoto, he used to send horses to Kifune shrine as offering to the god of rain. A black horse was sent as a prayer for rain to come, and a white horse was sent for the rain to stop. In modern times, it became troublesome to give and take care of many horses, so this may be the reason for the wooden ema tablets with horse images that are presented as prayer offerings nowadays.
 Further north in the village you will come across the Yui-no-yashiro or naka miya, the middle shrine. This is where Iwanagahime resides, the goddess of matchmaking. Rejected by a lover (to be fair, he wanted her younger sister only, not both of them), she angrily decided to help everyone else to find their match. And, many legends confirm her powers: Most famously, Izumi Shikibu, famed love poetess of the Heian period, prayed for love with a sad poem at the Yui-no-yashiro, and was promptly reconciled with her husband. Note that the sought-for relationship need not be romantic, connections between businesses, getting a new job, even having children, count as well.
Further north in the village you will come across the Yui-no-yashiro or naka miya, the middle shrine. This is where Iwanagahime resides, the goddess of matchmaking. Rejected by a lover (to be fair, he wanted her younger sister only, not both of them), she angrily decided to help everyone else to find their match. And, many legends confirm her powers: Most famously, Izumi Shikibu, famed love poetess of the Heian period, prayed for love with a sad poem at the Yui-no-yashiro, and was promptly reconciled with her husband. Note that the sought-for relationship need not be romantic, connections between businesses, getting a new job, even having children, count as well.
At the very end of the valley, and at the end of a lantern-lined foot path, lies the Oku-no-miya inner shrine. This is the spot of the original Kifune shrine, until a flooding in the 11th century forced people to move the main hall to its present location. According to legend, Kifune shrine came into being as follows: The goddess Tamayorihime, mother of first emperor Jimmu, appeared in Osaka Bay, and commanded that wherever her yellow ship would land, a shrine was to be built. And her ship went all the way via the Yodo and Kamogawa river to the end of Kibune valley, where the people indeed built a shrine and called it ki-fune, yellow boat. There is a prominent mound of stones to the left of the entrance to the Oku-no-miya, and legend has it that Tamayorihime’s yellow boat is buried beneath it.
 The Oku-no-miya is a rather special building, since it is built above a well called ryu ketsu (dragon’s cave). There are only two more shrines like that in Japan, in Nara and Okayama. Since the Oku-no-miya is a the very end of the valley, it is a wonderfully peaceful place surrounded by enormous trees making the spot truly mystic, regardless of the season.
The Oku-no-miya is a rather special building, since it is built above a well called ryu ketsu (dragon’s cave). There are only two more shrines like that in Japan, in Nara and Okayama. Since the Oku-no-miya is a the very end of the valley, it is a wonderfully peaceful place surrounded by enormous trees making the spot truly mystic, regardless of the season.
Kifune shrine is very popular among people whose businesses have to do with water: agriculture, fishing, brewing, dyeing; but also people working in fire departments, the Japanese marine, or as sailors come to pray to the god of rain and water here. When visiting Kifune shrine, ideally you first go to pay your respects at the Honguu main shrine, then at the Oku-no-miya inner shrine, and finally, on the way back, you pray at the Yui-no-yashiro.
Kifune shrine is worth a visit in any season. Since it is in the mountains, it is always cooler than in Kyoto city, which means snowy winters and breezy summers. Don’t forget to buy lucky charms! There is also a mizura omikuji to reveal your fortune – hopefully a good one – when placed in the water at the shrine.
